publications
2025
- Optimized Semantic Steering via Sparse Autoencoder AdaptersFarhang, A. R., Erickson, A. L., and Yue, Y.preprint 2025
We study the problem of steering LLMs, where the goal is to intervene on hidden layer activations in order to improve specific behavioral properties. We are particularly interested in settings where one can optimize over a large candidate set of steering interventions to find valuable, task-related perturbations. We take the approach of using sparse autoencoder adapters coupled with natural language feature descriptions to identify disentangled latent dimensions, after which we select and optimize a subset of the the latent codes that are relevant for the target downstream behavior. A key benefit of our approach is the ability to leverage LLM priors to guide feature selection without manual inspection of relevant features. We empirically demonstrate that our approach can generate steered LLM variants that outperform unsteered LLMs on natural language tasks. Furthermore, the selected steering variants can exhibit cross-lingual transfer, providing task improvements on other languages, unseen during selection or tuning. Our method enables tractable, optimized LLM steering by decomposing the problem into discrete feature selection and continuous optimization. This work demonstrates how tools from mechanistic interpretability can be leveraged to improve model capabilities.
2022
-
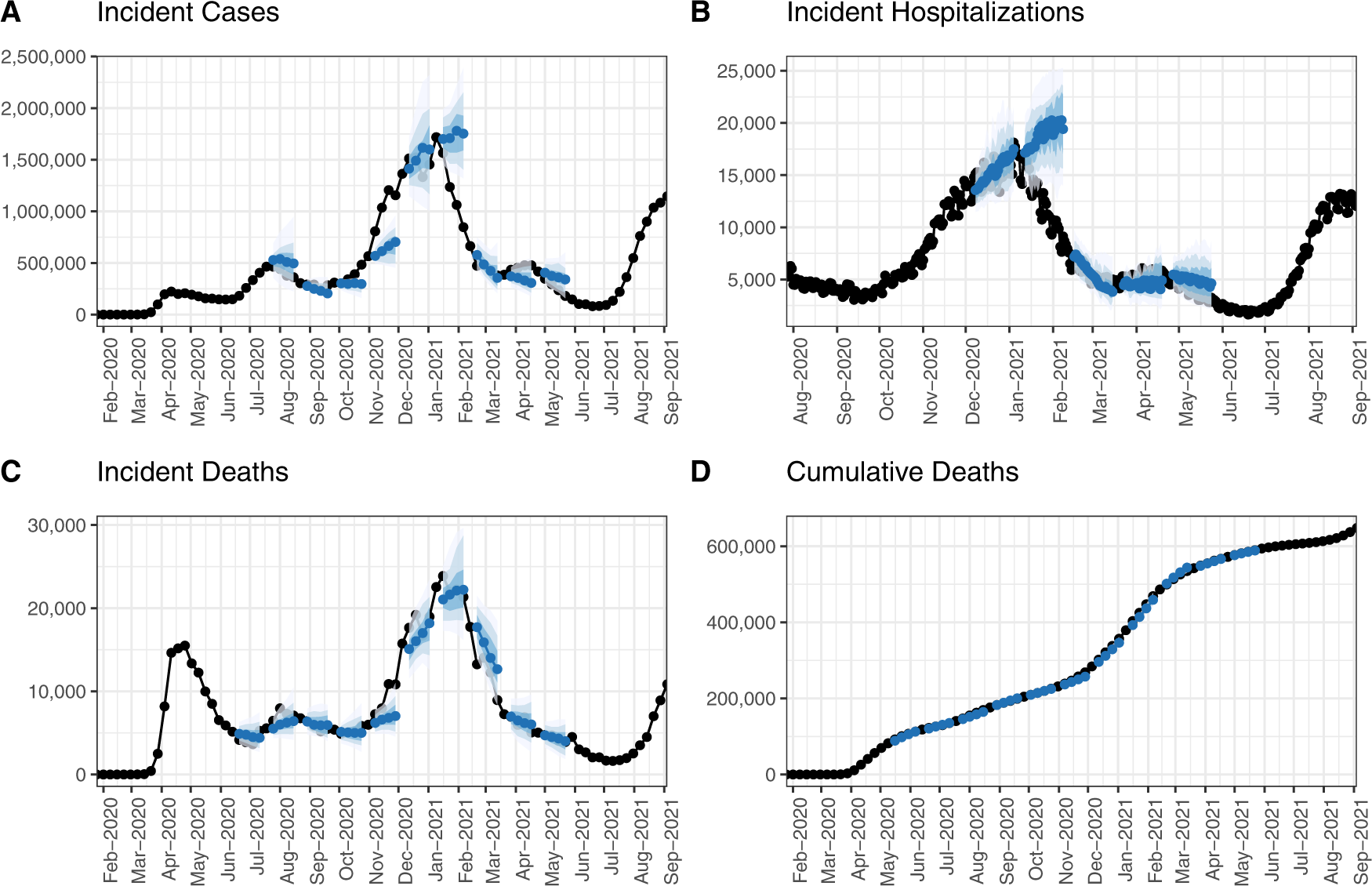 The United States COVID-19 Forecast Hub datasetCramer, Estee Y., Huang, Yuxin, Wang, ..., and US COVID-19 Forecast Hub Consortium,Scientific Data 2022
The United States COVID-19 Forecast Hub datasetCramer, Estee Y., Huang, Yuxin, Wang, ..., and US COVID-19 Forecast Hub Consortium,Scientific Data 2022Academic researchers, government agencies, industry groups, and individuals have produced forecasts at an unprecedented scale during the COVID-19 pandemic. To leverage these forecasts, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) partnered with an academic research lab at the University of Massachusetts Amherst to create the US COVID-19 Forecast Hub. Launched in April 2020, the Forecast Hub is a dataset with point and probabilistic forecasts of incident cases, incident hospitalizations, incident deaths, and cumulative deaths due to COVID-19 at county, state, and national, levels in the United States. Included forecasts represent a variety of modeling approaches, data sources, and assumptions regarding the spread of COVID-19. The goal of this dataset is to establish a standardized and comparable set of short-term forecasts from modeling teams. These data can be used to develop ensemble models, communicate forecasts to the public, create visualizations, compare models, and inform policies regarding COVID-19 mitigation. These open-source data are available via download from GitHub, through an online API, and through R packages.